The FMCSA designates 22 ELD-related violations that count against SMS scores.
In addition, full enforcement of the FMCSA’s ELD mandate is in effect, which means that ELD violations do affect CSA scores. Moreover, if a non-exempt driver doesn’t have an ELD when required, they’re also placed out of service for at least 10 hours.
That’s not a situation you’d want to be in.
In this guide, we take an in-depth look at the true “cost” of ELD violations, their impact on CSA scores, how you can avoid ELD violations, and more.
ELD violations and CSA scores
Different violations carry different severity weights. The following is a list of 22 ELD-related violations, along with the severity weight of each violation, that affect SMS scores.
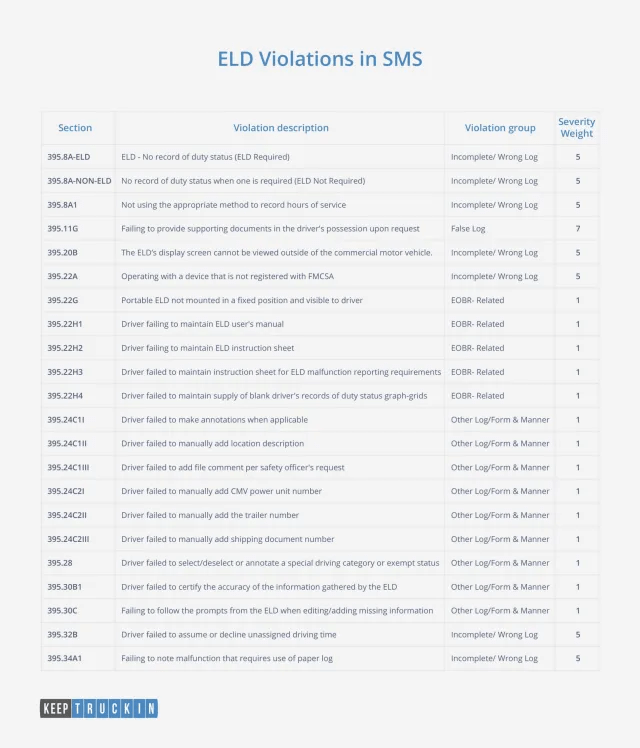
395.11G — “a failure to provide supporting documents in the driver’s possession upon request” carries the most violation points — 7 out of 10.
There are also a few smaller violations (severity weights of 1 out of 10), e.g., failing to make annotations, failing to manually add location description, failing to maintain an ELD instruction sheet, failing to maintain ELD user manual, etc. Although these violations are smaller in terms of severity weights, they shouldn’t be neglected.
With proper driver training and awareness, these violations can be easily avoided. For more information, read how to avoid ELD violations.
Drivers are being placed out of service
As we discussed earlier, if a non-exempt driver doesn’t have an ELD when required, they’re placed out of service for at least 10 hours. Additionally, drivers can also be placed out of service for:
- Using an unauthorized ELD
- Falsifying logs
Assuming that the driver at least has paper logs, they may be allowed to reach the final destination and deliver the load after the 10-hour out-of-service period is up. However, they can’t be dispatched on their next trip until they comply with the ELD mandate by installing an FMCSA-registered electronic logging device.
If a driver is dispatched again without an authorized ELD, the driver and the carrier may be subject to further enforcement actions.
The cost of violations and out of service
Each day is an estimated loss of $264 in revenue when a driver is out of service. Additionally, when a driver gets an out-of-service order, the vehicle will likely have to be towed. The cost of towing varies but a 40-mile tow, on average, could cost up to $344.
It is, of course, on top of all the fines and penalties you pay for the violation.
ELD violations result in a maximum civil penalty of $1,307 for each day the violation continues, up to $13,072.
Violations negatively affect your CSA scores, which, in turn, increases your chances of roadside inspections, and hampers your ability to get the best-paying loads and explore good business opportunities.
As you can see, violations can negatively affect your business in multiple ways. ELD violations directly cost you money in terms of fines, put your drivers out of service, and negatively affect your CSA scores.



