The retail industry has been forced to adapt quickly to constant disruption, and supply chain resilience has become a core focus. In 2024, retailers are using new strategies to tackle ongoing challenges like prolonged bottlenecks and extreme weather events, which can disrupt the holiday season.
Shifting priorities: Stability over cost-cutting

Retailers are prioritizing stability over cost savings, moving away from the traditional low-inventory restocking model. Instead, they’re restocking earlier and building extra inventory to shield themselves from disruption. A 19.7% year-over-year increase in Chinese imports by mid-summer underscored this shift, showing that businesses are willing to invest more to meet demand.
The surge in Chinese imports represents a broader trend in supply chain management. By sourcing earlier and holding more stock, retailers are preparing for the unexpected, especially during the high-stakes holiday season.
Mexico’s expanding role in U.S. retail supply chains
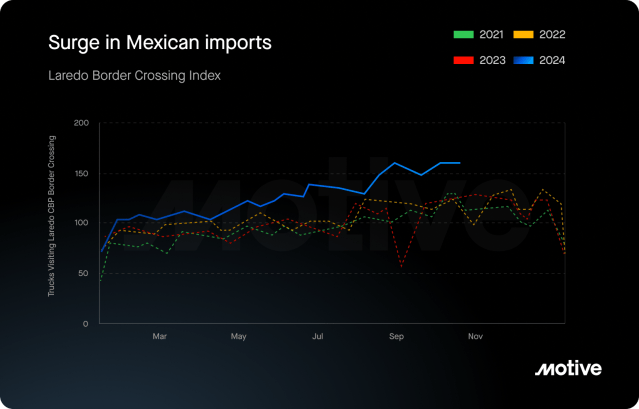
As retailers diversify their supply chains, Mexico’s become a key player. Motive’s September Economic Report shows a 30% year-over-year increase in imports from Mexico through the Port of Laredo. Retailers are turning to Mexico for its shorter lead times, lower tariffs, and to reduce the risks associated with other global supply chains.
By strategically balancing imports from both China and Mexico, retailers are minimizing risk and creating more resilient supply chains. Chinese imports help maintain inventory stability during high demand, while Mexican imports provide a quicker, more flexible option to avoid potential disruption.
As supply chain disruption becomes more frequent, proactive planning and diversification become more important. Retailers that adapt will protect their holiday sales — often accounting for 30% to 50% of annual revenue — and build more resilient supply chains in an unpredictable global environment.
| Our Take In 2025, we expect continued adjustments in inventory management and cross-border trade. Retailers are likely to further distance themselves from the just-in-time model, opting for higher inventory-to-sales ratios, which are predicted to climb above 1.3 by the end of 2024 and remain high throughout 2025. Meanwhile, imports from Mexico are expected to keep rising. Cross-border trucking activity will peak in early 2025. |
Early restocking and strong demand set up for growth
As the holiday season approaches, retailers expect a surge in consumer demand, supported by strong early restocking efforts that began in June. It was the first time since 2021 that the pre-holiday restocking blitz started so early, signaling that retailers are prepared for a successful season.
With a strong labor market, falling interest rates, and cooling inflation, consumers have a positive outlook. Spending has remained steady and shows no sign of slowing. Early restocking, combined with solid consumer confidence, suggests a booming shopping season ahead.
| Our Take Motive expects an increase in in-store shopping this holiday season, with brick-and-mortar stores seeing notable growth. |
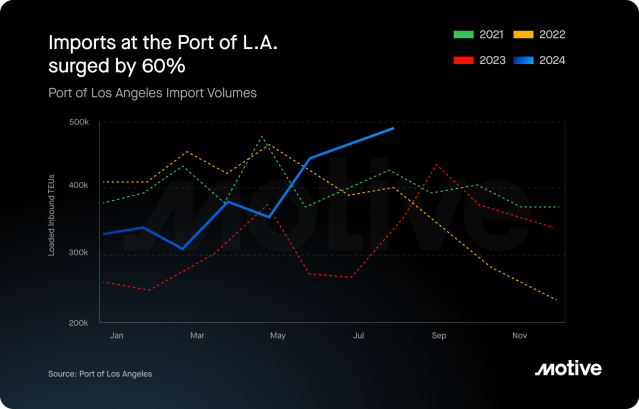
Following a brief two-day strike by the International Longshoremen’s Association, holiday sales are back on track. Thanks to a surge in imports through the Port of Los Angeles in July and August, sales are projected to grow by 5% to 8% this year.
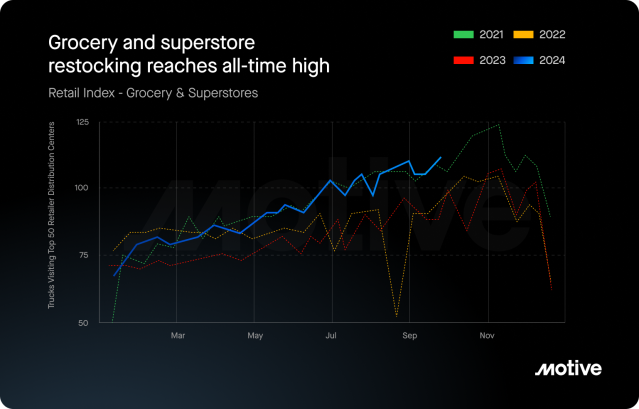
If summer trends persist, grocery, superstores, department stores, and home improvement retailers are set to drive the most growth. Grocery and superstores, in particular, hit an all-time high in restocking in August, up 22.6% year-over-year, while department stores and apparel surged by 27.1%. Home improvement stores saw an 11.2% month-over-month increase in restocking from August to September, reaching a 29.3% rise since 2023.
| Our Take As we move into 2025, retail prices are expected to rise, driven by increased freight and transportation costs. Retailers will pass these expenses on to consumers early in the year, even as inflation cools. |
Conclusion
The retail industry faces a complex landscape that rewards flexibility and proactive planning. From early restocking to strategic partnerships with Mexico, retailers are building strategies that will define their resilience in the coming years. Retailers that invest in robust, diversified supply chains and remain attentive to changing consumer demands will be best positioned to thrive in the face of future disruption.




